Circuit Design for a Highly Reliable Epi-Retinal Stimulator
In this project, the power efficient and area-optimized CMOS circuits for a highly reliable epi-retinal stimulator are developed. The goal of this epi-retinal stimulator is a capability of >1000 output channel including active charge balancing, ESD protection, and a flexible stimulation protocol. The high-voltage compliance stimulator output is based on a modified version of a voltage controlled resistor [M. Ghovanloo and K. Najafi, IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, Jan 2005], which is used in order to reduced the overdrive voltages of output devices - this consequently increases the voltage compliance, reduces the required voltage supply and therewith reduces the power consumption.
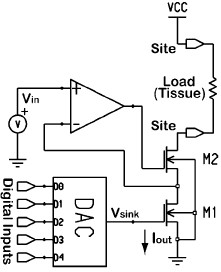
Due to imperfections of stimulator circuits, charge imbalance in stimulation current occurs, which must be prevented on long-term. Recently, we developed charge balancing which are based on an offset regulation technique and which shows a great long-term stability [K. Sooksood, T. Stieglitz and M. Ortmanns, IEEE ISCAS 2009]. The flexible control protocol is also currently developed, which steers the stimulation waveforms and also controls data distribution over the entire stimulator array. The generation of stimulation waveforms, the distribution of data and the execution of the stimulation protocol are realized using digital chip design.
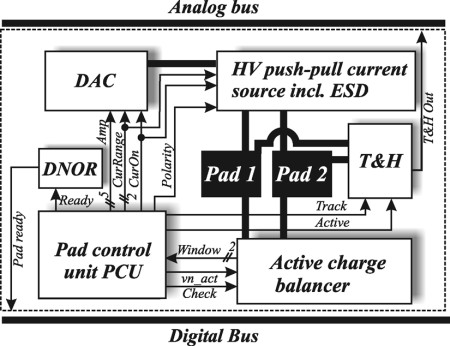
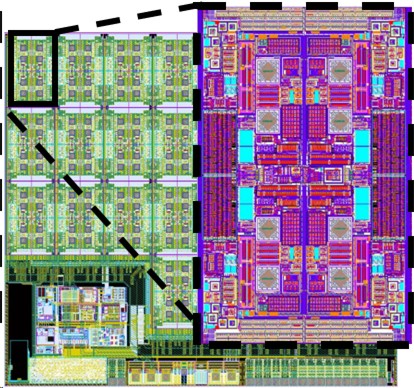
A first chip has been successfully implemented and published in IEEE JSSC, Dec 2007. The current work will enhance this ASIC both locally in the stimulator pixels, as well as globally in the common overhead circuitry, wireless telemetry and power management.
This work is funded by the Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) program “Intelligent Implant - FutureRet”. This project is conducted in collaboration with IMI GmbH, Bonn , Laboratory for Biomedical Microtechnology/IMTEK/University of Freiburg, and PVA TePla Analytical Systems GmbH.
Projektleiter
Ehem. Projektmitglieder
M.Sc. K. Sooksood
Dr.-Ing. E. Noorsal
M.Sc. H. Xu
M.Sc. Z. Lin
Partner
BMBF
IMI GmbH, Bonn
IMTEK, University of Freiburg
PVA TePla Analytical Systems GmbH
